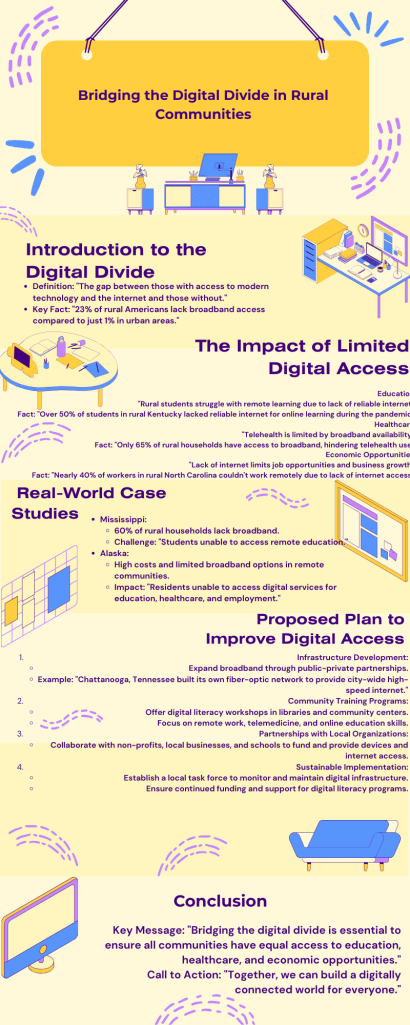
In our digital world, social media does more than just connect us—it can also spark change. Platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok have given people around the world a place to speak out against injustice and stand up for what they believe in. This blog highlights how the Black Lives Matter (BLM) movement used digital tools to become a global force, and introduces a new campaign called #RootedInResilience, focused on lifting up at-risk youth through storytelling and support.
Part 1: The Power of the Black Lives Matter Movement
The Black Lives Matter movement started in 2013 after the death of 17-year-old Trayvon Martin and the acquittal of George Zimmerman. It gained worldwide attention in 2020, following the killing of George Floyd. The movement’s main message is that Black lives should be treated with the same respect, safety, and justice as everyone else, especially when it comes to interactions with police.
Using Social Media to Take Action
BLM grew fast because it made smart use of social media. People shared powerful images, videos, and messages using the hashtag #BlackLivesMatter on platforms like Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook. Protesters were able to organize events quickly, raise money for victims’ families, and spread important information in real time. Online support helped the movement grow beyond the streets and into homes, schools, and government conversations.
What the Movement Accomplished
BLM didn’t just raise awareness—it created change:
- Protests happened in more than 60 countries
- More people began learning about systemic racism and the need for police reform
- Cities passed new laws, like banning chokeholds or funding better police training
Social media helped millions get involved. At its peak, BLM-related posts were being shared millions of times a day. Local BLM chapters were formed, and major media outlets covered their work. The world was listening.
Challenges Along the Way
Even with all its impact, BLM faced challenges:
- Some groups tried to spread false information about the movement
- Critics questioned its leadership and goals
- It became hard to keep the same momentum after the protests slowed down
Still, the way BLM used digital tools shows just how powerful online activism can be when done with purpose and passion.
Part 2: #RootedInResilience — Shining a Light on At-Risk Youth
Taking inspiration from BLM, a new campaign called #RootedInResilience aims to support at-risk youth—young people who deal with tough situations like poverty, trauma, abuse, or involvement in foster care or the juvenile justice system. This campaign doesn’t focus on what these youth are missing. Instead, it celebrates their strength, courage, and potential.
What the Campaign Wants to Do
The goal of #RootedInResilience is to:
- Share stories of youth resilience through photos, short videos, and quotes
- Connect youth to mentors and community resources
- Motivate adults to be positive role models and supporters
- Raise awareness about what these young people face and how we can help
By highlighting their strength instead of their struggles, this campaign hopes to change how people see at-risk youth—from victims to warriors.
Who It’s For and Where It Will Be Seen
This campaign is for:
- Young adults
- Educators, parents, and mentors
- Social workers and youth advocates
- Community organizations
To reach people where they already are, the campaign will use:
- Instagram and TikTok for quick, inspiring videos
- Twitter/X for updates, facts, and conversations
- Facebook to build community support and share longer stories
- YouTube for in-depth interviews and educational content
Creative Ways to Get People Involved
The campaign will include fun and meaningful activities to bring people in:
- Weekly Hashtag Challenge: Youth and mentors will post 30-second videos showing what keeps them “rooted” and resilient
- Digital Wall of Hope: A collage of photos, quotes, and artwork from young people and their supporters
- Mentor Minute Videos: Short clips where mentors explain why they give back and how others can do the same
- Partner Spotlights: Shout-outs to organizations that are already making a difference in young lives
These features are meant to build community, boost confidence, and inspire action—both online and in real life.
Tracking Our Success
To know if it’s working, the campaign will track:
- Online engagement (likes, shares, comments, hashtag use)
- Participation (how many people join challenges or sign up to be mentors)
- Real impact (testimonials from youth and mentors, new partnerships, and growth in online followers)
The goal is to spark more than just clicks.We want people to get involved, stay connected, and help change lives.
Closing Thoughts
Movements like Black Lives Matter show us how powerful a simple hashtag can become when people come together online and offline to demand change. In that same spirit, #RootedInResilience uses digital tools to uplift at-risk youth and show the world that their stories matter. They are more than their circumstances. They are survivors, leaders, and dreamers with so much to give.
We believe that every young person deserves to know:
You are strong. You are seen. You are rooted in resilience.
Let’s use our voices, our stories, and our platforms to help them rise.